Summary:
Laser is a high energy beam of light that can be used to cut or burn to treat eye disease. Burning laser can be used to treat leakage, new blood vessels or retinal tears. Cutting laser can be used to treat secondary cataracts or to perform refractive surgery. Laser treatments take only a few minutes. No special care is needed after most laser treatments. A special type of laser called photodynamic therapy (PDT) does require special care. An individual receiving PDT cannot be exposed to sunlight or intense lights for at least 48 hours or they are risk of developing a skin burn.
A more in-depth explanation of Laser Treatments
What is Laser Treatment?
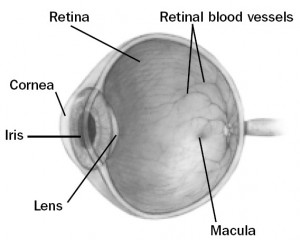 The word LASER stands for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation”. Laser is a high energy beam of light that can cut or burn tissue. There are many different types of lasers used to treat eye disease.
The word LASER stands for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation”. Laser is a high energy beam of light that can cut or burn tissue. There are many different types of lasers used to treat eye disease.
The general intent of laser surgery to the retina is to preserve your existing vision. The goal is to stop the progress of your eye disease. Do not expect it to improve your vision unless the doctor tells you it will.
At the doctor’s office you will have eye drops to enlarge your pupil and numb the front surface of your eye. Some laser procedures require an injection of freezing to numb the entire eye. You will sit at the laser in a dimly lit room, with your head supported by a chin and forehead rest. The doctor will place a special contact lens on your eye to focus the laser beam accurately. There is no incision or cutting into the eye. The doctor directs the laser light through the dilated pupil to the retina. Try to remain calm and do not move or squeeze your eyelids. When the doctor “fires” the laser, you may see a flash of light and feel a sensation of ache that can feel a bit uncomfortable. Sometimes the ache will feel like it is radiating backwards from your eye. The laser treatment usually takes from 5 to 15 minutes. No special eye care is required afterward. An eye patch is not necessary unless you had an injection of local anesthetic.
Your vision will be blurry for about 5-30 minutes following the laser. You do not have to remain at the office after your treatment. Arrange to have someone available to take you home. You may wish to wear dark glasses as your eyes will be sensitive to light while the pupil is large. You may take Tylenol if you experience any aching or irritation.
The doctor will need to see you again at some point following the laser to check your eye. More than one laser treatment is necessary in many cases to achieve the intended goal.
Laser treatment has been proven to be an effective method of reducing the risk of severe vision loss. Some types of peripheral laser treatment can cause swelling of the retina. This often results in blurring of vision which is usually temporary. Extensive treatment, necessary to treat certain eye diseases, can cause some peripheral vision loss and reduction in “night vision”, however most people do not notice this. Your doctor will discuss this with you if it is a possibility with your type of laser treatment. Every effort is made to keep visual loss at a minimum while controlling the disease process that is threatening your eyesight.
If you are receiving laser to repair a retinal tear, it is important to know that the laser will not remove floaters or haziness. The laser is used to seal the retinal tear, but is not able to remove blood, pigment or other debris floating in your eye. Time, usually a month or two will help to reduce the number and severity of floaters in your vision.
Ophthalmic laser surgery is a safe, precise and effective method of treating many retinal diseases. Your doctor will discuss your individual eye condition, treatment plan and expected outcome with you.